영신컨설턴트 (02) 529 8803 ystcha@naver.com 2021 7
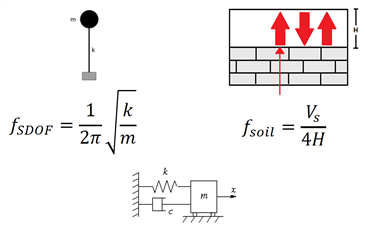
구조물의 고유 주파수(f)는 구조물 강성(k)과 질량(m)에 관계되고 구조물의 강성은 내구성 온도변화에 따라 달라 집니다. 구조물의 주파수를 상시미동으로 측정할 수 있습니다.
# 측정기
a small (1 dm3, <1 kg) all-in-one instrument, equipped with:
3 velocimetric channels (adjustable dynamic range) x y z 방향 속도계
3 accelerometric channels x y z 방향 가속도계
1 analog channel
GPS receiver
built-in radio transmitter/receiver 다수의 측정기를 동시에 무선 연결
구조물
f = 1/ 2 π root ( k/m)
f : 고유 주파수 k : 구조물 강성 m : 질량 c : 감쇄계수
지반
H : 연약지반 심도 (암반 깊이) Vs : 전단파 속도
구조물의 주파수는 k m c에 관련되고 고유 주파수와 감쇄 측정

상시미동으로 구조물의 자연 주파수 측정 NATURAL FREQUENCIES
다수의 측정기로 구조물 진동 형태 TYPES (bending 휨, rocking 흔들림, torsion 비틂)
FREQUENCY modal succession in slender and thick structures
다수의 측정기로 구조물 진동 형태 SHAPE
감쇄 DAMPING을 주파수에서 감쇄 c 측정
Ageing 주파수로 판단
Mass variation Stiffness variation 무게와 강성변화 시 주파수로 변화로 노후화 판단
Mass and stiffness variation 수리나 보강으로 무게와 강성변동 시 보강 전후 주파수 측정
Boundary conditions (thermal and environmental effects) 게절, 구속 조건의 변화
The dynamic behavior of a structure can be defined when:
modal frequencies (resonance frequencies, eigen-frequencies, natural frequencies……
modal shapes
modal damping
구조물의 고유주파수 (f0)와 주기 (T0)
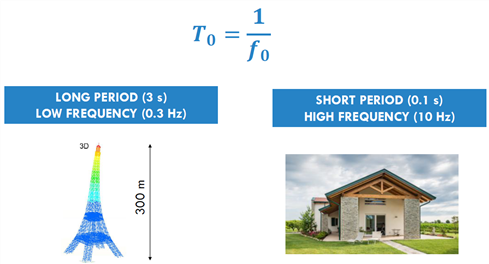
측정된 구조물의 고유 주기와 지역의 지진 가속도로 구조물의 안전 판단
RESPONSE SPECTRUM represents the maximum acceleration that a structure should resist according to its natural period of vibration and damping.
The y-axis (acceleration) depends on the seismic hazard of the construction zone.
지역의 지진가속도
The x-axis (eigen-period 구조물 고유주기 ) depends on the structural features.
The knowledge of the eigen-period of an existing structure allows the designer to read the corresponding acceleration value to withstand in the response spectrum
측정돤 주파수와 계산된 주파수 비교

intervention 구조물 수리 후 주파수 변화 측정

In some countries, measuring the eigen-periods is compulsory in BRIDGE DYNAMIC TESTING –BUILDING CODE, 2018 교량의 고유주기 측정 의무화

다수의 측정기로 동시에 진동형태 측정

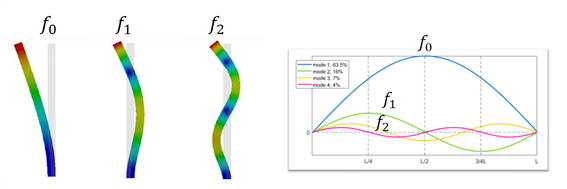
다수의 측정기로 bending mode of cantilever beam 빔의 휨 진동 측정

구조물의 높이와 폭에 따른 진동수

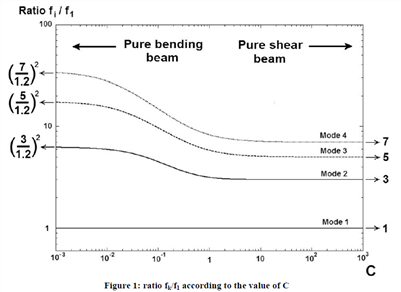
Thick beam :

slender beam :



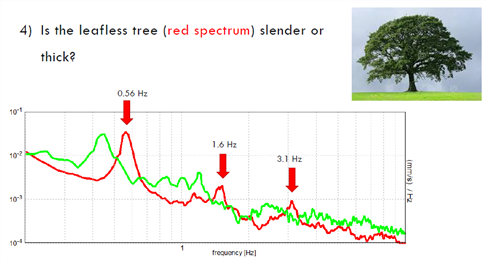
나무의 주파수

 CYDER |
 OAK |
These 2 trees have the same height (10 m).
1) which spectrum was acquired on the cyder? red (cyder, m down f up)
Which one on the oak ? green (oak, m up f down)
2) Which recording was acquired in winter (northern hemispehere)?
red (겨울 m down, k up, f up)
Which one in summer? green (여름 m up k down, f down)

3) Is the leafless tree (red spectrum) slender or thick? thick
f0=0.56 f1= 1.6 f2 = 3.1 f1/f0 =2.86 f2/f0 = 5.1

현수교 케이블 진동서 측정

추가 질량 시 주파수 변화 측정
to assess the effect of an additional mass on an oscillator
 |
 |
bending 휨 motion, Rocking 흔들림 motion
Rocking involves the ground.
In the case of rocking, the amplitude of the vertical motion at all levels is the same, while in the pure bending motion it decreases moving towards the bottom.
rocking 흔들림은 높이별 수직운동은 일정하고 bending 휨은 하부로 갈수록 휨이 작다.
Torsion 비틁 ( x y x 방향의 주파수가 유사)

진동 형태측정을 위한 다수의 측정기

온도변화에 의한 구조물의 강성이 다른 여름 가을 겨울 주파수 변동
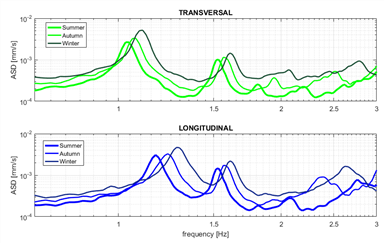
주파수
높이가 작은 구조물

높이가 큰 구조

나뭇잎이 있는 경우(mass 증가) 주파수 감소, 없는 경우( mass 감소) 주파수 증가
if we take ambient vibration measurements at different sites on a structure:
1) by performing the FFT of the recordings we get the modal frequencies
2) can we also reconstruct the modal shapes ?
5개의 측정기를 위치를 달리하여 동시 측정하여 진동형태 측정



해석 1차 연직방향 주파수 2.8Hz
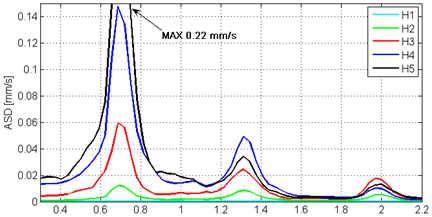
계산된 0.7 Hz 1st traversal bending mode

감쇄 (주파수)

'상시미동측정' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 상시미동에 의한 사장교(cable-stayed girder bridge,斜張橋)케이블의 주파수 측정과 인장력 (0) | 2021.08.12 |
|---|---|
| 지표면 표면파 시험 (0) | 2021.04.02 |
| 지반 구조물 내진설계 soil structure interaction (0) | 2021.03.23 |
| 지진경보 장치 (0) | 2021.02.09 |
| 지진경보 (0) | 2021.02.09 |