영신컨설턴트 (02) 529 8803 ystcha@naver.com 2020 8
압밀시험 원리
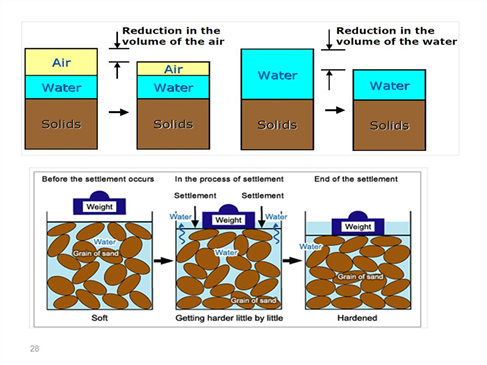
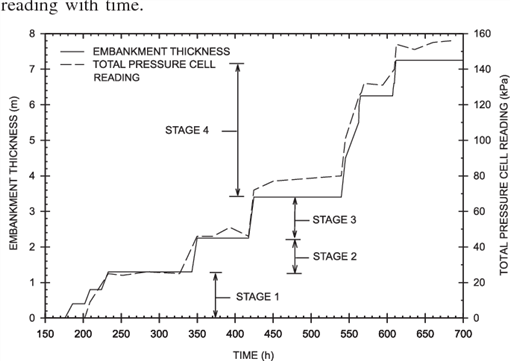
성토에 따른 압밀하중 증가와 토압 증가
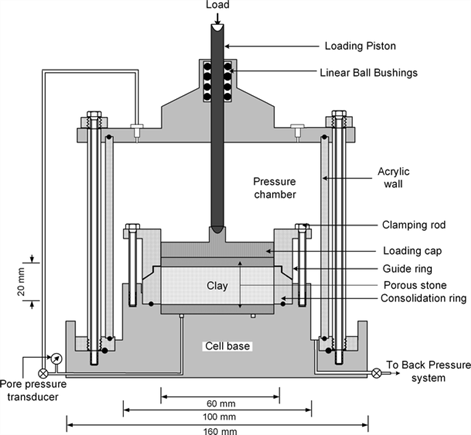
CRS시험 장점은 침하량 산정 위해 24시간 내 시험과 선행압밀하중이 정확하고 back pressure을 가하여 현장조건 유지하고 하단 간극수압 측정
CRS cell

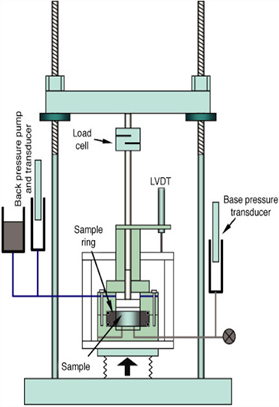
일반 압밀셀

CRS 장치 load frame, CRS cell, load cell, displacement, pore pressure

속도는 함수비 액성한계 예민비 강도에 따라 다르다.
water content, liquid limit, sensitivity and shear strength
a strain rate that generates a pore pressure ratio of 3-15%
??(Total vertical stress) 전응력 ??(Base excess pore pressure)
Swedish
standard rate of 0.680%/h,
higher rate of 3.00%/h and
lower rate of 0.154%/h
The Swedish standard (1991) for CRS test
strain rate ?̇ is 0.0025 mm/min, where an 18% deformation of the sample is obtained in 24 hours if the height of the specimen is 20 mm. However, the selected rate should be lower if the clay is very soft or muddy.
To be able to select the lower rate, the measured ??(Base excess pore pressure) must be supervised and can not exceed 10% of ??(Total vertical stress). On the other hand, ?? can be higher in some parts of the test, but not more than 20% of ??.
ASTM
standard is conducted, to determine whether the used strain rates is acceptable with in the range of ??⁄??=3 -15%.
The ASTM standard (ASTM, 2012) for the CRS test is called “Standard Test Method for One dimensional Consolidation Properties of Saturated Cohesive Soils Using Controlled-Strain Loading”
Selection of strain rate
The selection of an appropriate ?̇ is determined with the intention to produce a pore pressure ratio, ??⁄??,between 3% and 15% in the normally consolidated range throughout the loading phase of the test (Mesri & Feng, 2012).
Values for ??⁄?? higher than 15% is unacceptable to assure a fairly uniform distribution of ? and ?′? condition through the specimen height. When testing a new unidentified sample, it can be useful to change the rates during the first test and monitor ??to obtain an appropriate ?̇.

Methods for determining consolidation properties
Constant Rate of Strain (CRS) test
Incremental loading test (IL)

Constant pore pressure gradient (CGT) test
Aged normally consolidated clay
secondary consolidation will continue (Bjerrum, 1974)

The coefficient of consolidation, ??,
CRS구속하중에서 불포화토 흙수분 곡선 시험

삼축시험 불포화토 시험

'GDS' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Rowe and Bardon consolidation Cell 압밀시험 (0) | 2020.10.16 |
|---|---|
| Constant Rate of Strain (CRS) 변형율 제어 압밀시험 (0) | 2020.09.07 |
| 대구경 삼축 압축시험기 250kN Hydraulic Load Frame (0) | 2020.08.21 |
| 이방 응력 공진주 시험기 (0) | 2020.08.19 |
| 공진주 시험과 bender element 시험 결과 비교 (0) | 2020.05.21 |